What is Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)?
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) is a sophisticated technology that blends traditional automation techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) to create systems capable of handling complex tasks that usually require human cognition.
IPA leverages robotic process automation (RPA) to perform routine, rule-based tasks and improves these capabilities with AI technologies such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and cognitive decision-making.
IPA started gaining traction in the early 2000s as businesses looked to enhance efficiency. The automation was initially limited to simple, repetitive tasks that could be easily codified into software routines.
But, as the volume and complexity of data increased, it became evident that basic RPA could not handle processes involving unstructured data or decisions that required context understanding.
The integration of AI with RPA was a response to these limitations. AI technologies brought the capability to analyze large volumes of data, understand natural language, and make informed decisions based on patterns and context that were not explicitly programmed.
By the late 2010s, IPA systems had begun to take on tasks that were previously thought to be possible only for human workers, such as interpreting documents, making customer service decisions, and even predicting outcomes based on historical data.
Techopedia Explains the Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) Meaning
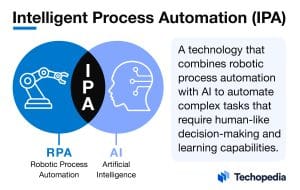
The simple intelligent process automation definition is a technology that combines robotic process automation with artificial intelligence to automate complex business processes that require human-like judgment and decision-making.
IPA uses machine learning, natural language processing, and cognitive computing to learn from data, make decisions, and manage workflows that involve both structured and unstructured data.
Today, IPA integrates fairly easily with existing systems, automating tasks across different platforms and bringing about digital transformation. This allows organizations to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and allow human employees to focus on higher-value activities.
So what is the meaning of intelligent process automation? It means a more streamlined experience for your customers and your organization.
How IPA Works
As mentioned earlier, Intelligent Process Automation works by combining the routine task automation capabilities of RPA with the cognitive abilities of AI. This fusion allows IPA systems to handle a wider range of activities, improving efficiency and decision-making within business processes.
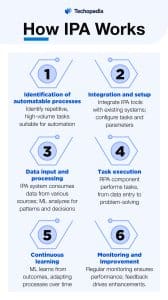
Here’s the step-by-step process of IPA in action:
Identification of Automatable Processes
The first step involves identifying business processes that are suitable for automation. These are typically repetitive, high-volume tasks.
Integration and Setup
IPA tools are integrated with existing IT systems. During setup, the specific tasks to be automated are configured, and the IPA system is programmed with the rules and parameters it needs to follow.
Data Input and Processing
As the IPA system operates, it consumes data from various sources. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to identify patterns and make decisions.
Execution of Tasks
The RPA component of IPA executes the configured tasks. Depending on the complexity, these might range from data entry and form submissions to more complex problem-solving tasks.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
IPA’s machine learning aspect continuously learns from the outcomes of its actions. Over time, the system adapts to changes in data or conditions, optimizing its processes to increase efficiency and accuracy.
Monitoring and Improvement
Regular monitoring ensures that the IPA system is performing as expected. Feedback from this monitoring leads to continual adjustments and improvements in the automation scripts and AI models.
What Technologies Does IPA Use?
Intelligent Process Automation uses a mix of advanced technologies to automate complex business processes and improve decision-making capabilities.
To recap, here’s a brief overview of the key technologies involved:
What Are the Components of Intelligent Process Automation?
Software robots are the operational units in Robotic Process Automation necessary for carrying out repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry and file manipulation.
These robots interact with digital systems in the same way a human would, which allows for improved speed and accuracy.
AI engines act as the intelligent core of an IPA system, using machine learning algorithms and complex data processing to make autonomous decisions, learn from results, and continually improve processes.
These engines are important for allowing IPA systems to manage complex tasks that require sophisticated, adaptive responses.
Decision engines are specialized components of an IPA system focused on making logical decisions from analyzed data. They process information from various sources, applying pre-set rules and learned data patterns to make informed decisions quickly.
Analytics and data capture tools are tasked with collecting and analyzing the large volumes of data these systems use. Data capture tools gather inputs from multiple sources like emails and databases, while analytics tools process this data to extract actionable insights, monitor system performance, and evaluate the success of automated processes.
These tools make sure that IPA systems have the necessary information to perform optimally and adapt to new challenges.
IPA vs. RPA
Intelligent Process Automation and Robotic Process Automation are both valuable tools in automation, but they serve different functions, and each has its own capabilities.
Intelligent Process Automation Examples
IPA is used across various industries. Here are a few real-world examples.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, IPA is used to streamline patient intake processes and manage electronic health records. A notable case study involves a large hospital network that implemented IPA to automate the scheduling and tracking of patient appointments.
The system uses natural language processing to interpret and respond to patient inquiries via email and text, majorly reducing administrative workload and improving patient satisfaction.
Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions use IPA for fraud detection and compliance monitoring. A major bank, for example, uses IPA to analyze transaction patterns in real time, identifying anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities.
The IPA system integrates machine learning models that adapt based on new fraud tactics, helping the bank stay ahead of security threats while minimizing false positives.
Retail
In retail, IPA improves supply chain management and customer service. One retail giant implemented IPA to optimize its inventory management system.
The IPA solution processes sales data across various channels to accurately predict stock levels, automates ordering processes, and manages distribution logistics, resulting in reduced overstock and stockouts.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing firms use IPA for predictive maintenance and quality control. A case study in this sector involves an automobile manufacturer that has integrated IPA into its production lines.
The system monitors equipment performance using sensors and AI to predict when maintenance is needed, thereby reducing downtime and maintaining product quality standards.
Telecommunications
Telecommunication companies use IPA for network management and customer service operations. A telecom operator that uses IPA to manage network traffic and optimize bandwidth allocation dynamically is a good example.
This proactive approach ensures high service quality and customer satisfaction by adjusting resources in real time according to user demand patterns.
Implementing IPA in Organizations
You’ll need to plan carefully if you want to implement IPA into your organization successfully. It involves the right tech tools, effective training, and strategies to overcome potential challenges.
IPA Pros and Cons
As with everything, there are pros and cons to IPAs.
Pros
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Improved accuracy
- Scalability
- Enhanced customer experience
Cons
- High initial investment
- Complexity in integration
- Resistance to change
- Ongoing maintenance and training
The Bottom Line
Intelligent Process Automation combines robotic process automation with advanced AI to improve business efficiency by automating complex processes. It boosts productivity, improves accuracy, and offers scalability, transforming not only how tasks are completed but also making customer service better and adjusting employee roles towards more strategic activities.
Businesses that integrate and adapt to IPA effectively will likely see considerable gains in operational efficiency and competitive advantage, despite the challenges of high initial investment and integration complexities.